As companies migrate more workloads to the cloud, managing costs and extracting optimal value from their investments has become a significant challenge. This blog aims to demystify FinOps and explore 20 strategies for effective cloud cost optimization. We delve into each category in detail, complete with examples from the top three cloud providers – Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). By understanding these strategies and implementing them effectively, businesses can achieve a balance between speed, cost, and quality, transforming their cloud economics for a sustainable and competitive edge.
Let’s delve into these FinOps optimization strategies –
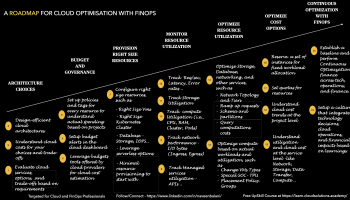
- Understanding Cloud Usage: Understanding the usage of cloud resources helps identify underutilized resources, thereby controlling costs. AWS Trusted Advisor, Azure Advisor, and Google Cloud Operations Suite (formerly Stackdriver) offer insights into resource usage and provide optimization recommendations.
- Cost Visibility: Gaining visibility into where and how spending is happening is crucial for cost management. AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Cost Management and Billing, and Google Cloud’s Cost Management tools help track, analyze, and manage cloud costs in detail.
- Demand Forecasting: Forecasting future cloud usage helps in better planning and decision-making. AWS offers Cost Explorer Forecasting, Azure uses Cost Management’s Cost Analysis, and Google Cloud uses BigQuery ML for creating demand forecasting models.
- Budgeting and Reporting: Setting clear budgets and regularly reporting on costs enables businesses to avoid overspending. AWS Budgets, Azure Cost Management’s Budgets, and Google Cloud’s Budgets & Reports facilitate cost monitoring against defined budgets.
- Governance and Compliance: Ensuring compliance with regulatory and internal governance rules is essential. AWS Config, Azure Policy, and Google Cloud’s Policy Intelligence provide compliance monitoring and governance.
- Procurement Optimization: Effective procurement strategies can lead to significant cost savings. AWS Savings Plans and Reserved Instances, Azure Reservations, and Google Cloud’s Committed Use Contracts offer discounted rates compared to on-demand pricing.
- Performance Efficiency: The efficiency of cloud resources directly impacts costs. AWS Compute Optimizer, Azure Advisor Performance Recommendations, and Google Cloud’s Recommendations Hub suggest ways to improve performance and reduce costs.
- Lifecycle Management: Managing the complete lifecycle of cloud resources prevents unnecessary costs. AWS Systems Manager, Azure Resource Manager, and Google Cloud’s Deployment Manager assist in automating lifecycle processes.
- Cost Allocation: Accurate cost allocation to various business units promotes accountability. AWS Cost Allocation Tags, Azure’s Cost Tags, and Google Cloud’s Labels facilitate the assignment of costs to specific teams, projects, or departments.
- Automation: Automating routine tasks saves time and reduces the risk of human error. AWS Lambda, Azure Logic Apps, and Google Cloud Functions support automating tasks like cost reporting or compliance checking.
- Performance Monitoring: Regular performance monitoring of cloud resources ensures optimal use. AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, and Google Cloud’s Operations Suite offer real-time monitoring of resources.
- Security Optimization: Maintaining optimal security measures prevents expensive breaches. AWS Security Hub, Azure Security Center, and Google Cloud Security Command Center provide comprehensive threat protection for cloud resources.
- Resource Optimization: Regular review and optimization of resource allocation lead to cost efficiency. AWS’ Right-Sizing Recommendations, Azure’s Cost Analysis, and Google Cloud’s Compute Engine Rightsizing Recommendations help optimize resource allocation.
- Employee Education: Regular training sessions on cost-effective practices in cloud usage can reduce costs. AWS Training and Certification, Azure Learn, and Google Cloud Training offer educational resources to help users understand cost implications better.
- Data Backups and Compression: Regular data backups and the use of data compression can save storage costs. AWS S3 Glacier and EBS Snapshots, Azure Backup and Blob Storage, and Google Cloud Storage’s Coldline and Archive storage classes offer efficient data backup and storage solutions.
- Container Optimization: Optimizing containerized applications can lead to cost savings. AWS ECS & EKS, Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), and Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) offer capabilities to manage and optimize container workloads.
- Network Optimization: Effective network management practices ensure optimal performance and cost savings. AWS Transit Gateway, Azure Virtual WAN, and Google Cloud’s Cloud Interconnect, and Cloud CDN help optimize network performance and manage network costs.
- Disaster Recovery Planning: Planning for potential service disruptions helps prevent financial losses. AWS Disaster Recovery, Azure Site Recovery, and Google Cloud’s Disaster Recovery Planning guide provide strategies for data recovery and business continuity.
- Sustainable Computing: Sustainable practices can reduce environmental impact and sometimes costs. AWS’s Sustainability Pillar, Azure’s Well-Architected Framework, and Google Cloud’s Carbon Sense Suite support sustainable cloud computing practices.
- Multi-Cloud Deployment: Using multiple cloud providers can increase reliability and cost savings. Tools like Google Anthos enable applications to be deployed uniformly across different cloud services, providing flexibility and avoiding vendor lock-in.
By understanding these strategies and implementing them effectively, businesses can achieve a balance between speed, cost, and quality, transforming their cloud economics for a sustainable and competitive edge.